Protein research
The ABS of molecular engines
To date, five steps of a complicated transport mechanism had been known. Researchers from Bochum have now discovered a sixth one.
Peroxisomes are cell organelles that carry out a number of functions, including the degradation of cytotoxins. For this purpose, they require enzymes that have to be transported into peroxisomes via complicated machinery. The team from the research group Biochemistry of Intracellular Transport Mechanisms at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) headed by Professor Harald Platta has detected an as-yet unknown transport step, thus gaining a better understanding of life-threatening diseases. The group published its report in the renowned journal Biochimica et Biophysica Acta – Molecular Cell Research in February 2019.
Vital importance
Peroxisomes are cell organelles of vital importance. Providing an insulated reaction chamber for more than 50 enzymes, they are linked to numerous cellular processes. The main function of peroxisomes is the degradation of long-chain fatty acids and cytotoxins. “In addition, they also fulfil highly specialised functions, for example in the synthesis of penicillin in fungi, the formation of lysine in yeasts, the photorespiration of plants and the generation of plasmalogens for the white matter of the brain in animals,” explains Harald Platta. Defects in the formation of functional peroxisomes lead to severe metabolic disorders in humans, which often result in infant death.
The engine of the import machinery
In order for peroxisomes to fulfil their functions, they have to import the relevant enzymes inside first. Most enzymes are guided into the respective peroxisome by the import receptor Pex5p. That receptor is controlled by the protein ubiquitin (Ub) that attaches itself to the receptor temporarily.
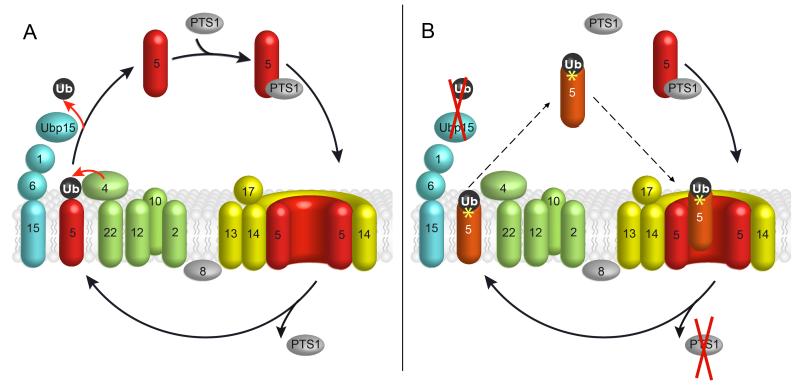
“To date, we have been able to break down the import mechanism into five steps,” elaborates Harald Platta: “First, the binding of Pex5p to the imported enzyme in the cytoplasm. Second, the binding of the Pex5p enzyme complex with the peroxisome. Third, the enzyme being released inside the peroxisome. Fourth, Ub attaching itself to Pex5p. And fifth, the export of Ub-modified Pex5p into the cytoplasm to enable further import reactions.”
The ABS of molecular machines
The attachment of a Ub molecule to Pex5p plays a crucial role for the import cycle. Energy is required for this step, as well as for the subsequent export of the complex. “In previous publications, we have described the Ub attachment to the import receptor as an accelerator pedal, as it were,” says Platta.
Figure
However, it had remained unclear what exactly happened to the exported Ub-modified Pex5p. The current study, which is based in the first place on the PhD projects of Rebecca Brinkmeier and Fouzi El Magraoui, has provided an answer to this question. By analysing systematically generated Ub and Pex5p variants, the team demonstrated that a stable Ub-Pex5p fusion causes a defect in the peroxisomal protein import. Accordingly, Ub has to be detached from Pex5p again.
Once ubiquitin has been taken over by another enzyme, Pex5p reverts to its original status and can be reused. If this step is missing, the import receptor spins out of control. First, it careens inside the cytoplasm as a complex, until it erratically crashes back into the peroxisome where it blocks the docking complex, thus inhibiting the import of the correct Ub-modified Pex5p. “Eventually, this leads to complete loss of function in the peroxisome,” concludes Platta. “Our study thus adds the necessary sixth step to the import cycle.”